Description
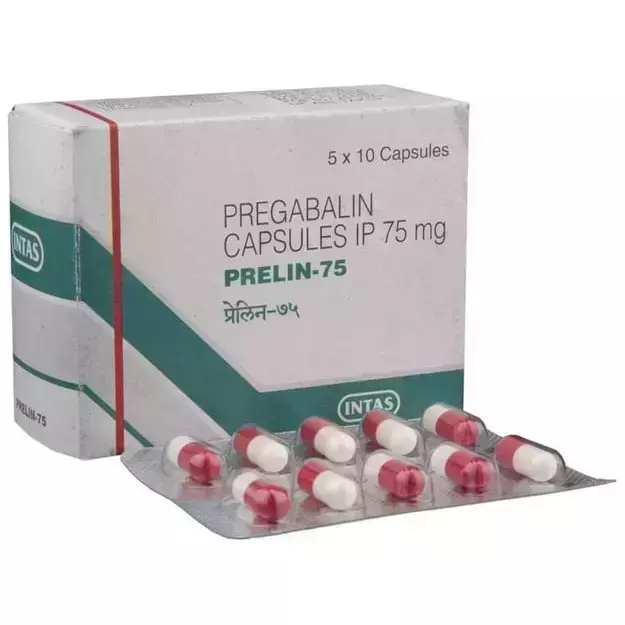
Uses of Pregabalin 75 MG Capsules:
Pregabalin 75 MG Capsules is a medicine designed to address various nerve-related conditions. It effectively manages neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) and postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), offering relief from chronic nerve pain. Approved as an adjunctive therapy for partial-onset seizures in patients as young as 1 month, Pregabalin 75 MG Capsules also alleviates fibromyalgia symptoms, enhancing the quality of life. Additionally, it treats neuropathic pain linked to spinal cord injuries, making it a trusted choice for improving comfort and well-being in diverse patient groups.
Dosage & Side Effects:
Pregabalin 75 MG Capsules is administered orally, with or without food. Gradually taper the dose over at least one week when discontinuing.
For neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, start with 50 mg thrice daily (150 mg/day); increase to 300 mg/day within one week based on efficacy and tolerability. Do not exceed 300 mg/day due to dose-dependent adverse effects.
For postherpetic neuralgia, start with 75 mg twice daily or 50 mg thrice daily (150 mg/day); increase to 300 mg/day within one week. In select patients, doses up to 600 mg/day may be considered with caution. Adjust doses for patients with reduced renal function.
Adjunctive Therapy for Partial-Onset Seizures in Patients 1 Month of Age and Older: The recommended dosage for adults (17+ years) starts at 150 mg/day, up to 600 mg/day in 2–3 doses. For pediatric patients, doses vary by weight: ≥30 kg (2.5–10 mg/kg/day) and <30 kg (3.5–14 mg/kg/day), divided appropriately.
The most common side effects of Pregabalin 75 mg Capsules are dizziness, somnolence, dry mouth, edema, blurred vision, weight gain, and cognitive issues like difficulty concentrating. In pediatric patients treated for partial-onset seizures, increased weight and appetite are the most frequently reported side effects.