Description
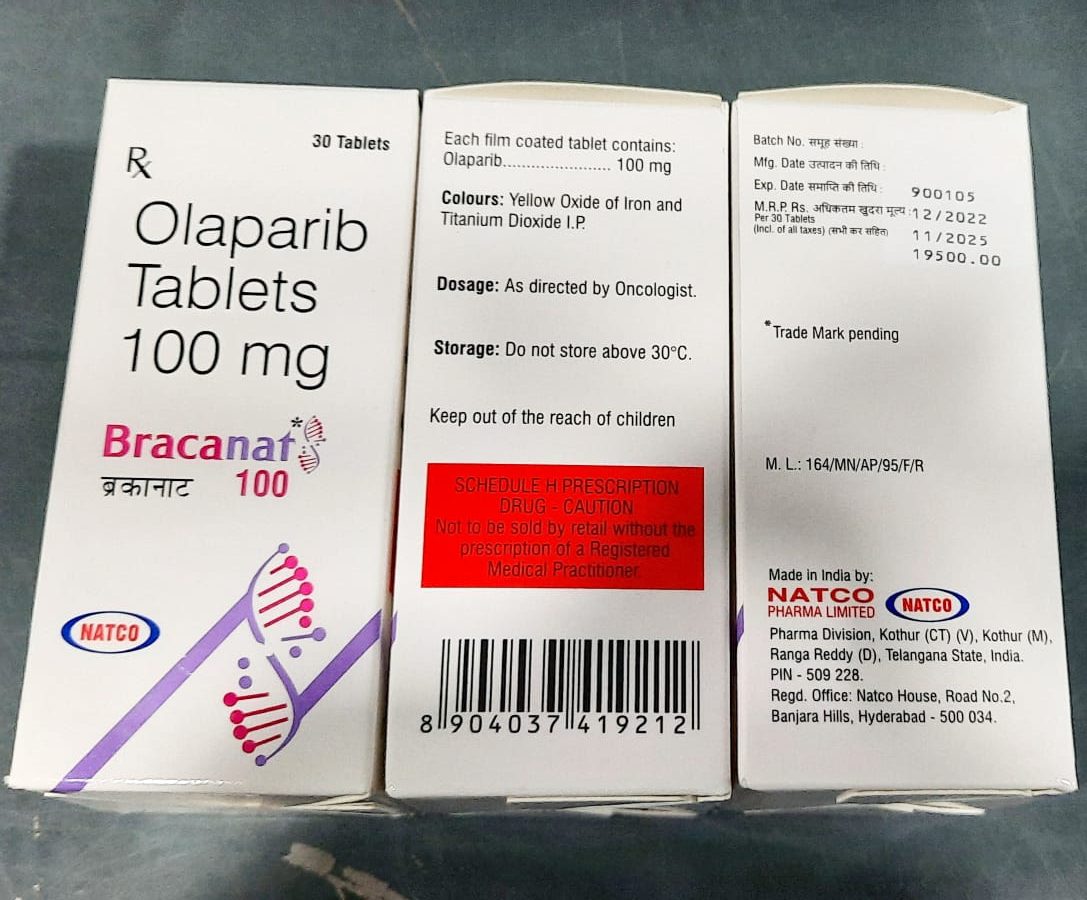
Olaparib Uses:
Olaparib is a poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor. Olaparib is an inhibitor of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) enzymes, including PARP1, PARP2, and PARP3. PARP enzymes are involved in normal cellular functions, such as DNA transcription and DNA repair. Healthcare professionals recommend using this medicine in treating patients with ovarian cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, and prostate cancer.
Dosage:
This medicine comes in the form of tablets to administer orally via the mouth in the standard strengths of 100 mg and 150 mg. The recommended dosage of Lynparza is 300 mg taken orally twice daily, with or without food. If a patient misses a dose of Lynparza, instruct the patient to take the next dose at its scheduled time. Instruct patients to swallow tablets whole. Do not chew, crush, dissolve, or divide the tablet.
Side Effects:
The common side effects of Olaparib are vomiting, nausea, fatigue, anemia, diarrhea, decreased appetite, cough, headache, neutropenia, abdominal pain upper, dysgeusia, dyspnea, dizziness, dyspepsia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia. Side effects of Olaparib in combination with Bevacizumab were fatigue, nausea, anemia, lymphopenia, diarrhea, vomiting, neutropenia, urinary tract infection, leukopenia, and headache.
Warnings and Precautions:
- Cases of the incidence of Myelodysplastic Syndrome/Acute Myeloid Leukemia (MDS/AML) have been observed in patients receiving Olaparib. Do not start Olaparib until patients have recovered from hematological toxicity caused by previous chemotherapy (≤Grade 1). Monitor complete blood count for cytopenia at baseline and monthly thereafter for clinically significant changes during treatment.
- The incidence of pneumonitis, including fatal cases, was observed by healthcare professionals in patients receiving Bracanat. If patients present with new or worsening respiratory symptoms such as dyspnea, cough, and fever, or a radiological abnormality occurs, interrupt Lynparza treatment and promptly assess the source of the symptoms. If pneumonitis is confirmed, discontinue treatment with Olaparib and treat the patient accordingly.
- Olaparib can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman based on its mechanism of action and findings in animals. Healthcare professionals advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 6 months following the last dose of Olaparib.